This article provides you the sources of Methane Emissions in the USA its Mitigation Efforts and challenges. Methane (CH₄) is a potent greenhouse gas (GHG) with a global warming potential many times greater than carbon dioxide (CO₂) over a 20-year period. In the USA, methane emissions come from a variety of sources.
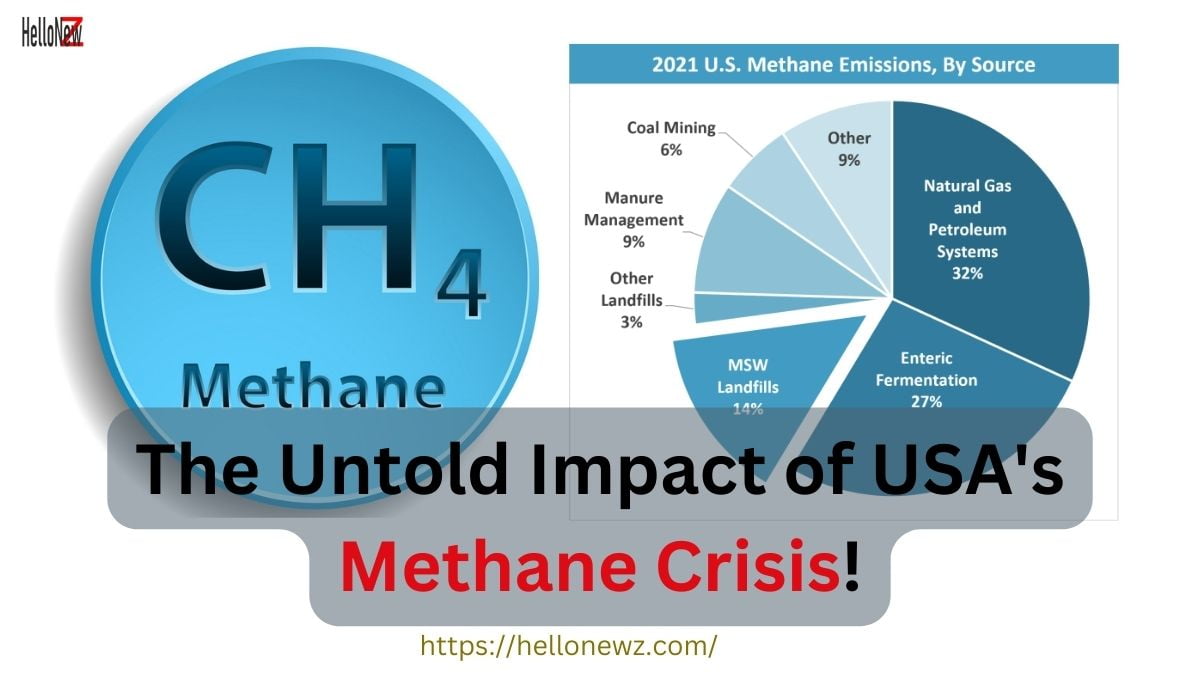
Major Sources of Methane Emissions in the USA:
Let’s dive deeper into each of the major sources of methane emissions in the USA.
- Enteric Fermentation in Ruminants: This digestive process occurs predominantly in animals such as cows, goats, and sheep. During this process, microbes residing in the stomachs of these ruminants ferment their food, producing methane as a byproduct. This methane is then belched out by the animals. Given the large cattle industry in the U.S., especially beef and dairy farming, this source of methane is considerable. Interventions in diet and breeding can influence the amount of methane produced by individual animals.
- Natural Gas and Petroleum Systems: Methane emissions from this sector arise from both intentional activities and system inefficiencies. During the extraction, processing, storage, and transportation of natural gas and crude oil, methane can either leak unintentionally from faulty equipment or be vented intentionally during specific operational activities. This source is particularly significant due to the prominence of the U.S. in the global oil and gas industry. Innovations in drilling and extraction technology, as well as rigorous monitoring, can help reduce these emissions.
- Landfills: As organic waste decomposes in landfills without the presence of oxygen (anaerobically), methane gas is produced. Given the scale of waste generated in the U.S., landfills remain a notable source of methane. However, many modern landfills now employ methane capture systems, turning this waste gas into an energy source or flaring it to reduce its greenhouse effect.
- Coal Mining: Methane is naturally present in coal seams and can be released during mining activities. While coal mining in the U.S. has seen a decline in recent years, it remains a source of methane emissions. Mines can employ degasification systems to reduce the release of methane, and post-mining activities can further minimize emissions.
- Manure Management: When livestock manure decomposes, it produces methane, especially when the decomposition occurs in anaerobic conditions such as in liquid storage. The type of livestock, their diet, and the manure management system all influence the quantity of methane emitted. By employing different waste treatment and storage methods, these emissions can be mitigated.
- Wastewater Treatment: Municipal wastewater and certain types of industrial wastewater contain organic matter. In the absence of oxygen, as this matter breaks down, it emits methane. While wastewater treatment plants in the U.S. are increasingly capturing this methane for energy use, there remains potential for further reductions.
In essence, while each of these sources poses challenges, they also present opportunities for interventions and innovations to reduce methane emissions. With the right combination of technology, policy, and industry practices, the U.S. has the potential to make significant strides in decreasing its methane footprint.
Methane emissions had seen fluctuations. Technological advancements and increased efficiency in the oil and gas industry, as well as improved agricultural practices, have contributed to some reductions. However, growth in certain industries and a lack of stringent regulations in some areas led to continued emissions.
Also Read: The Phenomenon of the “Ring of Fire” Solar Eclipse 2023
Mitigation Efforts:
- Regulation: The EPA has established guidelines and regulations to monitor and reduce methane emissions from various sectors, especially oil and gas.
- Technological Advancements: Technologies like methane capture at landfills or improved efficiency in natural gas extraction have helped to reduce emissions.
- Alternative Practices: In agriculture, practices like rotational grazing, diet modifications for cattle, and efficient manure management can help reduce emissions.
- Awareness & Education: Increased awareness among stakeholders and the public can lead to more proactive measures to reduce emissions.
Challenges of Methane Emissions in the USA
- Economic Implications: The transition to low-methane practices, especially in the energy sector, can have economic implications, potentially leading to job losses or increased costs.
- Regulatory Gaps: Not all methane sources are equally regulated, leading to gaps in mitigation efforts.
- Data Accuracy: Monitoring and verifying methane emissions can be challenging, leading to potential underestimations.
Methane is a significant contributor to global warming, and the USA, with its vast energy and agricultural sectors, plays a crucial role in global methane emissions. While steps have been taken to curb these emissions, continued effort, investment, and public-private cooperation are essential to see meaningful reductions.